A microwave oven, better known as a microwave oven, is a useful kitchen appliance that makes everyday life much easier. Having it in your arsenal, you won’t have to spend a long time fiddling around in the kitchen heating up food. A microwave oven is also called a microwave oven.
The purpose of this household electrical appliance is to quickly prepare or quickly heat up cooked food and defrost food. Compared to a classic oven, for example, an oven, a microwave oven heats food not from the surface, but throughout the entire volume.
Microwaves, penetrating deeply into almost any food, reduce heating time significantly. The article will discuss the operating principle and design of this equipment, which is indispensable in the kitchen.
How does a microwave oven work?
To understand this, a little background information is needed. Most food products contain the following substances: salts, fats, sugar, water. In order for microwaves to “work”, that is, to heat food, the food must contain dipole molecules.
On the one hand they have a positive electrical charge, on the other - negative. There are enough of these molecules in food - these are fats and sugar, but the main dipole is a water molecule.
Vegetables, meat, fruits and fish contain a large number of dipole molecules, the number of which reaches millions. If there is no electric field, the molecules are arranged in a chaotic order.
In microwave ovens, microwaves have a frequency of 2450 MHz
In the presence of an electromagnetic field, they begin to “line up”: “plus” is directed in one direction, “minus” in the other. When the field changes polarity, the molecules “unfold” 180 degrees.
In microwave ovens, microwaves have a frequency of 2450 MHz. 1 hertz = 1 oscillation per second. Megahertz is a million vibrations. The polarity changes twice during one wave period.
When food is exposed to microwave radiation, the molecules in it begin to rotate more often, literally rubbing against each other. This releases heat, which serves as a source of heating for the food.
The heating of food by microwaves can be compared to the way your palms heat up when you rub them together. “Waves” affect only the surface layer of food, penetrating no deeper than 1–3 cm.
But the heat “goes” further – the physics of thermal conductivity comes into play. This also leads to advice: if you need to heat up a large piece of meat, it is better to set the microwave oven to medium power. This way it will warm up better, although it will take longer. Heat from the outer layers will begin to penetrate inside.
The situation is similar with soups: it is better to periodically remove them from the oven and stir them, helping the heat to penetrate inside.
The stove models currently being produced may have a “Double Radiation” function - this indicates a bifurcated radiation source. Thanks to this separation, the products are heated more evenly, and the microwave oven has increased efficiency.
Microwave oven design
Now it's time to figure out how a microwave works. The heart of any such stove is a special generator that creates a high-frequency electromagnetic field of high intensity. It's called a magnetron. Next, the field created by it is directed to the product chamber using specially designed waveguides. He does this in such a way that the entire internal volume of the chamber is “filled” with the field evenly, ensuring high-quality heating of products of any volume. Additionally, this is facilitated by the rotating tray that most microwave ovens are equipped with.
The magnetron occupies the most honorable place under the lid of the device.
The operation of the HF generator is controlled by an electronic unit assembled on a microprocessor. The microprograms built into the unit allow you to set the desired cooking mode, control the temperature in the chamber, humidity, and cooking time. They also monitor the safety of using the stove - whether the protective door is closed, whether there is an insulation breakdown, whether the temperature inside the chamber has risen above critical, etc. The controller is controlled from one type of remote control or another - push-button, touch, etc. And, of course, , the furnace also has a power supply that supplies energy to all the electronics and the magnetron itself.
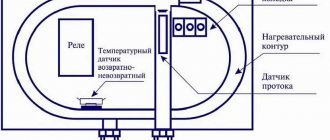
This is what a microwave oven looks like on the diagram.
Microwave oven diagram
A good example is the Samsung RE290D microwave oven. A schematic electrical diagram will help you understand how furnaces from any manufacturer work. They can differ only in specific modifications. The diagram itself is shown in the photo.
On the left side, it is noticeable that the grounding contact of the plug is connected to the housing, and it is connected from the middle point of the capacitor decoupling filter, which reduces interference from high-frequency radiation.
In the area of the power input there is a soft type fuse - FU1. To check its condition, they use electrical methods - they test the circuit with a multimeter operating in ohmmeter mode.
There is a second fuse that protects the microwave from operation in emergency mode, for example, when the door microswitches are faulty.
In order for the magnetron, the radiation source, to start “working,” the door service contacts open, and all the others close. If you turn them off, any of them, the supply voltage will be removed from the high-voltage transformer.
The circuit has thermal fuses-sensors (2 pcs.), which, depending on the temperature of the magnetron housing and the working chamber, open and close. The first one has periodic work. It protects the magnetron from overheating. The second one is triggered if the fan is faulty or the ventilation holes are clogged.
Microwave Samsung RE290D
The safety relay contact provides connection to the electric motors of the timer and cooling fan. If the Monitor Fuse blows, the relay coil will fail.
The switch responsible for selecting power is located on the timer. He, following the algorithms, removes the voltage from the magnetron circuit.
Resistor R1 briefly reduces the starting current of the transformer. This requires a working Inrush Relay contact.
Its task is to limit the pulse caused by the discharge of the capacitor (it can receive a charge before it turns on). This ensures that the microwave oven starts smoothly.
The power circuit of this oven from Samsung is simple for those who understand it. The main difference in microwave ovens is the electronic units, with different designs and functionality.
Microwave device
There are several required parts inside the microwave, so it’s a good idea to know what their role is. The internal structure has the following design: a metal chamber in which food is heated and a door that prevents radiation from escaping outside.
To ensure that food is heated more evenly, the chamber is equipped with a rotating table powered by a gearbox (motor). But there are other important details.
Control block
Microwave control unit
The control panel is:
- mechanical;
- electronic
The control unit maintains the specified power and turns off the device after the specified time.
Inside the electronic unit there is a microcomputer with rich potential, so during the production of furnaces it finds other uses. For example, they build in a clock or excerpts of melodies that signal the end of work.
The control unit is a circuit with which a person directly interacts. The working bodies are: buttons, mechanical switches, regulators, with the help of which operating parameters are set. Through them the power is set, the mode and program are selected.
The circuit itself is structured differently. The simplest one is a circular controller, one of which is a timer. There is also a hybrid system - with buttons. It is more functional compared to “mechanics”.
A control unit in the form of a touch panel is increasingly common. The principle of operation is similar to mechanical buttons, only more reliable. Advanced circuits support “programming” - the power and time of radiation output are adjusted.
Microwave radiation generation unit
This is the “heart” of the microwave oven. The element looks like a vacuum tube, which could be found in old CRT televisions.
Its task is to generate an intense high-frequency electromagnetic wave. When electrons pass through a magnetic field, a wave is formed, the length of which varies.
The generation unit does not include the only microwave source. In order for the waves to enter the working area of the furnace, waveguides are provided in it. They are located behind a mica plate, which is “hidden” behind the side wall.
Primary and secondary protection systems
Monitoring sensors ensure that key electronics and hardware are working properly and not in emergency mode. Their function is to ensure trouble-free operation of the microwave oven and prevent dangerous failures.
Control sensor
To protect people from exposure to microwaves, microwave ovens have a locking mechanism consisting of several switches:
- Primary Switch;
- Secondary Switch;
- Door Switch;
- Monitor Switch.
The unit generating microwave radiation will start working only when the contacts of the primary and secondary switches are closed (the door is closed).
The purpose of the door switch is to block the operation of the power control relay. It is installed mainly in equipment with an electronic control unit.
Microwave functions
Heating food in the microwave
Most people use a microwave oven simply to heat food. But this technique is capable of more. With its help, you can even cook barbecue, grilled chicken, bake potatoes, and so on.
The only thing is that the “grill” mode requires a power of 1500 W, which means there will be a lot of light to “pull” the oven. And the magnetron, the unit that generates radiation, does not last forever.
Therefore, the less often you use the stove, the longer it will last. Nowadays, it is rare that anyone completely abandons traditional stoves in favor of microwaves.
List of functions available in microwave ovens and their purpose:
- movable grill. Allows you to change the angle of inclination. Those who prefer grilled chicken choose ovens with this function;
- convection. Blowing hot air over food. According to the manufacturers, this function is intended for baking. True, stove models with it are expensive, heavy and bulky. It’s not surprising, since a rather large fan is placed behind the equipment, pumping air;
- bio-coating. Otherwise - ceramic coating, although manufacturers call them differently. Its advantages: durability, strength, biological inertness (microbes will not multiply inside the oven, even if it is not washed for a long time). The more expensive the microwave model, the more sophisticated its coating;
- auto cooking. This is a feature found in LG technology. There are fully automated programs designed for preparing a specific dish. For example, porridge is being prepared. With this mode, all that remains is to select the weight of the product, and the power and time will be set automatically;
- defrosting. It's simple - the oven operates at the minimum power required to defrost food;
- Intellowave. A system that allows you to heat food evenly, for example a large piece of meat. Built-in sensors “monitor” individual areas of the product, determining surface temperature and adjusting power;
- steam supply An additional feature that prevents food from drying out during cooking;
- ventilation of the working chamber. Useful if you want to prevent the new dish from becoming saturated with remaining odors.
These are the basic functions, but new ones are constantly being added to them.
Microwave ovens solo
A solo microwave oven is nothing more than a simple appliance for one person. We are not talking about any cooking, built-in programs, and so on. The only thing you can do in most of these models is heat up food.
Pros:
- Low cost - due to the simplest device;
- Only for heating food - no need to understand additional settings.
They differ from other types of microwave ovens in that they have different microwave powers and designs. The power of solo microwave ovens varies from 100 W to 1450 W. Their size is usually small, which is extremely convenient for a small kitchen.
As standard for solo models, an internal acrylic or enamel coating is used. Both are easy to keep clean. Some solo models also involve defrosting frozen semi-finished products.
What is a magnetron
A magnetron in a microwave oven is an element that generates high-frequency radiation in the working chamber. The electromagnetic waves emitted affect the molecules contained in the food, causing it to heat up. That is, heating does not require external thermal influence.
It is for this reason that the temperature in microwave ovens does not exceed +100 degrees Celsius. The magnetron is the main part that sometimes fails. It can be replaced with a new one, but for this, full compatibility in power, frequency, and terminal location is taken into account.
Magnetron operating principle
A microwave oven works like this: it converts electrical energy into high-frequency electromagnetic radiation. As a result, the water molecules contained in the food begin to “move”, which leads to heating. The device that generates microwaves is called a magnetron.
Microwave Magnetron
A magnetron is often compared to an electric vacuum diode, which operates due to the phenomenon of thermionic emission. The phenomenon occurs when the surface of the cathode or emitter heats up.
High temperature “forces” active electrons to leave the surface. But for this to happen, voltage must be applied to the anode.
The generated electric field sets the electrodes in motion, which are directed along the power lines to the anode. An electron that finds itself in a magnetic field changes its trajectory.
The magnetron anode is made in the form of a cylinder with cavities. Inside it is a cathode with an incandescent filament. At the edges of the anode there are ring magnets that form a magnetic field. Because of them, electrons are not able to move directly from the cathode to the anode.
Their trajectory is disrupted and they begin to rotate around the cathode. Electrons passing near the resonators give them part of their own energy (interchangeability). As a result, a powerful microwave field is formed in the cavity, which is brought out through a wire loop.
The magnetron “starts” when a high voltage of 3000–4000 V is applied to the anode. For this reason, in household electrical networks the magnetron must be connected through a high-voltage transformer.
Magnetron device
Magnetron is an element responsible for the generation of high-frequency oscillations. There are devices with a similar principle of operation - klystrons and platinotrons, but they have not received proper distribution.
The magnetron was first used in a microwave oven in 1960. Currently, a multicavity element is used. Its components and their descriptions:
- anode. A copper cylinder consisting of several sectors. It has resonator cavities that create a ring oscillation system;
- cathode. A cylinder with a filament located in the center of the magnetron. This part is responsible for the emission of electrons;
- ring magnets. Located at the ends of the oven. They create a magnetic field directed parallel to the magnetron. The electrons move in the same direction;
- wire loop. It is located in the resonator, connected to the cathode and output to the emitter antenna. The purpose of the loop is to output high-frequency radiation into the waveguide. From there it goes into the working chamber of the microwave.
Magnetrons have a simple design, so they are used not only in microwave ovens, but also in radar.
The operating principle of a microwave oven. Reference
The first microwave ovens, intended for army canteens and large restaurants, were cabinets 175 cm high and weighing 340 kg. More compact home stoves began to be produced in 1955.
The first mass-produced household microwave oven was released by the Japanese company Sharp in 1962. Initially, the demand for the new product was low. In the USSR, microwave ovens were produced by the ZIL plant.
The operating principle of a microwave oven is based on the processing of a product placed inside the device with microwaves (microwave radiation). These waves heat the food.
Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic energy, just like light waves or radio waves. These are very short electromagnetic waves that travel at the speed of light (299.79 km/s).
Food contains many substances: mineral salts, fats, sugar, water. To heat food using microwaves, it must contain dipole molecules, that is, molecules that have a positive electrical charge at one end and a negative one at the other. There are plenty of similar molecules in food - these are molecules of fats and sugars, but the main thing is that the dipole is a molecule of water - the most common substance in nature. Every piece of vegetables, meat, fish, and fruit contains millions of dipole molecules.
In the absence of an electric field, the molecules are arranged randomly. In an electric field, they line up strictly in the direction of the field lines, “plus” in one direction, “minus” in the other. As soon as the field changes direction to the opposite, the molecules immediately turn over 180 degrees.
The magnetron that every microwave oven contains converts electrical energy into an ultra-high-frequency electric field of 2,450 megahertz (MHz) or 2.45 gigahertz (GHz), which interacts with water molecules in food.
Microwaves bomb water molecules in food, causing them to spin millions of times per second, creating molecular friction that heats the food.
This friction causes significant damage to food molecules, breaking or deforming them. Simply put, microwaves cause breakdown and changes in the molecular structure of food through the process of radiation.
Microwaves work only in a relatively small surface layer of food, without penetrating deeper than 1-3 cm. Therefore, heating of products occurs due to two physical mechanisms - heating of the surface layer by microwaves and subsequent penetration of heat into the depth of the product due to thermal conductivity.
When choosing a microwave oven, you should focus on its main characteristics, including chamber volume, type of control, presence of a grill, power and some others. The volume of the chamber is determined by the number of products that fit into the microwave oven.
There are three types of controls in microwave ovens - mechanical (the simplest type of control), push-button and touch.
Depending on the functions they perform, microwave ovens are divided into three types: microwave ovens, grill ovens, and grill and convection microwave ovens.
As for the additional functions of microwave ovens, the most common ones include the functions of double radiation (for uniform cooking of the product by volume) and auto-weight, which means that electronic sensors will weigh the product and select the cooking time.
Some models of microwave ovens have an interactive mode, when recommendations are displayed on the display while cooking a dish.
There may also be a microwave oven with built-in cooking recipes. To start the cooking process, you need to specify the type of product, quantity, and recipe. Ready-made programs make it possible to choose the optimal mode and exact cooking time.
Some models are equipped with a communication port for Internet access. This makes it possible to download new recipes and receive information about its calorie content.
Microwave oven accessories may include a multi-level plate rack, which allows you to heat several dishes at the same time, and a grill rack.
The material was prepared based on information from open sources