Often, when buying a refrigerator for their home, most people are only interested in the appearance and price, and only then the power consumption of the refrigerator. As statistics show, a significant part of buyers make their choice in favor of a famous company, thereby justifying the huge costs of advertising. Many people don't realize that a cooling appliance's electricity use accounts for about 30% of monthly consumption. Every year, savings become more and more relevant, and when purchasing, it would be useful to pay attention to the power consumption in kilowatts (kW), because the refrigerator is constantly connected to the network and consumes electricity 24 hours a day, 365 days a year.
The characteristics of the device are indicated in the instructions for the refrigerator, but if you do not have it at hand, they can be found on the information sticker located on the back wall or inside the refrigerator compartment. The average power is in the range from 100 to 200 watts per hour, this power is enough to maintain a temperature of -5°C in an environment of +25°C.
What function is affected by the power of the refrigerator?
The power of a refrigeration unit directly affects its energy efficiency and also affects the operation of its additional functions.
Energy efficiency is determined by the rational use of electricity by a device. Thus, a class A refrigerator consumes an average of 100 watts per hour, 1.5 kW per day, and over the course of a year this figure can vary between 365-550 kW. What consumption you reach depends on how correctly the owner uses his refrigerator.
Freezing power is an indicator that determines how much food (in kg) the freezer is able to freeze in one day.
The information sticker contains information with the indicator “X***”. The number of stars next to the symbol depends on the amount of food being frozen. The freezing power rating is measured in kilograms per day and indicates the amount of food (in kg) that it can cool to a temperature of -18°C in 24 hours. The default room temperature of food is +18-20°C. For ordinary household refrigerators, when used in a single-family home (of 3-4 people), the freezing capacity should not be lower than 9 kg/day.
Electricity consumption calculations
The values of consumed electricity depend on the number of refrigeration chambers (the more chambers, the more electricity is required to cool them), on the cooling system (compressor, absorption, thermoelectric, gas) and other characteristics.
Compressor refrigerator calculations
The minimum average power of a compressor refrigerator ranges from 100 to 200 W/hour, and 300 W/hour is the maximum, that is, the average is about 250 W/hour.
In 1 minute the refrigerator consumes 4.17 W : (250 W / 60 minutes). This is under normal conditions, the temperature in the refrigerator compartment should not fall below +5°C, and the temperature in the room should not exceed +25°C.
We recommend: Electric meter plugs
But since the refrigerator does not work all day, but only when the temperature drops, in about a day the device consumes a minimum of 1.5 kW, a maximum of 3.5 kW, and an average value of 2.5 kW per day.
This comes out to 75 kW per month: 2.5 (consumption per day) * 30 (days in a month).
Depending on the region, electricity tariffs may differ, so we take an approximate value of 3.75 rubles. for 1 kW/hour, multiplied by monthly consumption: 3.75*75=281.25 rub.
Based on calculations, for using a refrigerator with a power of 250 W per month you will need to pay 281.25 rubles.
For absorption refrigerator
The normal minimum power is 75 W, and the maximum is 200 W, with an average value of 135 W/hour.
Consumption in 1 minute: 135/60=2.25 W.
Approximately 0.85-1.5 kW per day comes out, we take 1.2 kW per day.
Consumption per month: 1.2*30=36 kW.
Payment amount: 36*3.75=135 rub.
Car refrigerators
Also, car refrigerators have recently gained great popularity. They are small in size and have low power, which makes them possible to use during trips and travel.
The average power of such a refrigerator is 45 W/hour.
We recommend: What is UUTE in a housing and communal services receipt?
For one minute of operation, the power consumption is 0.75 W: 45/60 minutes.
During the day it consumes about 360 W.
This comes out to 10.8 kW per month: 360*30 = 10800 W.
Payment amount: 10.8 * 3.75 (for example, the tariff for 1 kW/hour, there are different tariffs in each region, district, city and village) = 40.5 rubles.
Due to their small volume and good thermal insulation, they consume little electricity, but they are not suitable for home use due to their small capacity.
All they need is a connection to a car battery to maintain the cold inside the chamber.
Important! These calculations are made based on average statistical data and depending on the manufacturer’s model and the power consumption of the refrigerator, these values may vary.
What are the classes?
An inexperienced consumer can easily get confused about energy efficiency classes. Moreover, the instructions were revised more than once, becoming more complicated each time. Since 2014, amended standards have been in force, dividing devices into classes (table below).
The table shows that the higher the class, the lower the percentage value of the index, and at the same time the energy consumption of the model.
Important! This gradation applies exclusively to refrigerators and free-standing freezers. Other equipment (washing machines, split systems, etc.) operates with different indicators.
Class A
A little earlier, equipment was classified by letters from A to G. Over the last ten years, even more economical products with a reduced index have appeared. Therefore, pluses began to be added to the letter A - from one to three. Models with this index today occupy almost two-thirds of the entire refrigeration market.
It turns out that equipment in the same category can have completely different energy efficiency. That is, Class A refrigerators are considered energy-saving, while A+++ devices are more than twice as superior to them in this regard: 50% versus 22% (see table).
BG classes
There are still equipment on sale with energy efficiency class B-D. But in five to ten years no one will remember about them, as happened with the EG category models. Naturally, it is not advisable to buy a refrigerator with a high energy efficiency index (B or C).
Advice! The best option for the budget and mid-budget segment is A+ or A++. Almost all premium models come with the prefix A+++.
Efficiency class
The efficiency class is usually understood as a conditional indicator that characterizes the electrical energy consumption of a refrigerator. To designate this class, capital Latin letters were adopted: starting from A and ending with G. The following three classes have recently been added to the old 7 classes (A+++, A++ and A+). The efficiency of these classes is higher than A. Thus, the power of a refrigerator in kW hours per year for the LG brand, which belongs to class A, is 350-360 kW per year.
The values given for these letters determine the average power consumption of the refrigerator. This so-called average power consumption of a refrigerator for a class D refrigeration unit is taken as 100%. Relative to this class, the energy consumption values, measured in kWh, for class A are 55% less, for A+ by 65, A++ - 85 and A+++ - 95%. For convenience, refrigerator manufacturers highlight all the classes under consideration in color. The differences between classes in the electrical energy they consume are significant.
The video describes the efficiency classes of modern refrigerators: from A+++ to D in order of decreasing efficiency. It is also said that the stationary cooling system is more economical compared to No Frost.
Annual energy consumption of the refrigerator
Such equipment works year after year and consumes expensive kilowatts day and night. The larger and more functional the equipment, the more electricity it consumes.
To calculate the annual consumption, it is necessary to clarify the power of the device or the peak load current. All data of this kind must be indicated in the instruction manual or brief specification, which is presented on the box.
If the documentation has not been preserved, then you can estimate the approximate consumption taking into account the energy saving class:
- A – 150-300 kW;
- B – 350-600 kW;
- C/D – 600-900 kW.
To calculate your energy costs, you need to multiply these figures by the current tariffs for your region. For example, if you have an A+ class refrigerator in a Moscow apartment, you will have to pay 807 rubles per year: 150 kW * 5.38 rubles. While for equipment of category B you will need to pay about 2000 rubles: 400 kW * 5.38 = 2152.
You can also calculate the annual consumption by knowing the load current. We calculate the power (amps * volts) and, taking into account the average operating time of the compressor per day (about 6 hours), we get an approximate value in kW. For example, 1.2 A * 220 V = 264 W = 0.26 kW. Next, 6 hours * 0.26 = 1.56 kW per day. We multiply the resulting figure by the number of days in a year, and then by the tariff (in our case for the capital - 5.38). In total, you need to pay 3063 rubles per year: 365 d * 1.56 kW = 569.4 kW * 5.38 = 3063.
Main energy consumption classes
Back in the 90s, all modern household appliances began to be divided according to the newly introduced energy consumption classification. This equally applies to both miniature light sources and large water heating tanks and washing units.
Now labeling indicating the class inherent in a particular device is mandatory.
By looking at the sticker placed on the surface of the appliance, you can quickly find out how much electricity the refrigerator you like consumes per year, depending on its power. Such information must be duplicated in the technical data sheet of the unit.
On average, annual electricity consumption in kilowatt-hours is in the range of 235-465 kW. Knowing the parameter, calculating the approximate daily or monthly figures is not difficult.
To do this, it is enough to divide the declared value by the number of days/months in a year - 365/12. For example, if a device consumes 230 kW/h annually, then the daily rate is approximately 0.63 kW/h. Monthly calculations are carried out using a similar principle.
To see the most accurate statistics, you should consider a small margin of error. It is usually recommended to add three tenths to the number obtained in calculations
letters ranging from A to G. Each of them is assigned a color graphic indicator for a more understandable perception. Some designations are supplemented with the index “+” .
The gradation is determined by dividing the actual amount of consumption by the standard indicator. The first figure is established during experiments.
The second is obtained as a result of calculations using a complex formula, which involves many components - volumes of departments, temperature, technologies used, climate class, etc. Information is provided to the user in the form of a percentage of energy consumed for a specific time period to specified standards.
The ABC of energy consumption of refrigerators looks like this:
- A+++ – up to 22%;
- A++ – 22-33%;
- A+ – 33-42%;
- A – 42-55%;
- B – 55-75%;
- C – 75-95%.
The most economical and rational equipment is considered to be category A with a green indicator of different shades, the most expensive is G , marked in red. Units A+ , A++ , A+++ consume three times less than generally accepted standards.
Devices below class C are practically no longer produced, as they are malicious wasters of light. The energy consumption of such refrigerators is from 110 to 150% . These values are far from the norm and can cost a pretty penny.
in terms of energy consumption includes equipment marked B and C. It saves approximately 15 to 35% of resources.
In addition to the class and annual percentage of energy efficiency, the refrigerator label contains information about the internal volume of the cabinets, noise level, model name and manufacturer
The difference between refrigerators classified into different classification categories can be quite significant. A type A++ requires only 143 kWh per year, while its fellow G consumes more than 900 kWh over the same period.
A+++ , which are 50% more economical than even equipment that has an A+ , will help you save your family budget . It is quite natural that they cost an order of magnitude higher, but the subsequent savings will soon pay for the investment in the purchase with interest.
How to choose an economical model
It is impossible to calculate the specific energy consumption of a refrigerator using bare data taken from technical documentation alone. Especially when we are talking about models from the budget and mid-budget segment. The number of kilowatts consumed is also influenced by the features of internal systems.
Factors responsible for energy consumption:
- compressor;
- cooling system;
- volume and number of chambers;
- tightness;
- additional functionality.
Important! Even such a convenient addition as a display adds tangible values to the total kilowatts. Not to mention modes like super freezing.
Compressor
On sale you can find models with one or two compressors. The latter offer more efficient control of temperature conditions - the number of modes and the speed of cold injection. Naturally, a tandem consumes much more electricity than a single unit.
As for the type of unit, inverter compressors are considered more economical . Such devices lower the temperature quite quickly and maintain the set values without much expense, smoothly adjusting the power.
Inverter compressors do not create serious loads on the network, operate relatively quietly and fail much less often than their analogues. Classic devices (stepped) always use full power both to increase the temperature and to maintain it.
Cooling system
Today's models operate on two technologies - NoFrost and a drip cooling system. In the latter case, the block with the evaporator is mounted on the rear wall of the refrigerator. Melted ice drops drop by drop onto a special tray and subsequently evaporates.
NoFrost technology works through dry freezing. That is, ice or frost does not form on the walls. The evaporation system is installed either behind the chambers or above the freezer. The liquid accumulated during operation is transported through gutters into a tray, after which it turns into steam. In this case, no forced defrosting of the refrigerator is required.
The drip system is more economical, while the NoFrost technology implies greater convenience, as well as several kilowatt-hungry fans and heating coils.
On a note! There are models where both systems work in pairs, complementing each other. This is a kind of compromise between ergonomics and energy saving.
Volume and number of chambers
The optimal solution for the average family of 3-4 people is a two-chamber refrigerator with a separate freezer. Models with one compartment will come in handy in a small kitchen. The more cameras and their volume, the higher the energy consumption. Therefore, when buying a refrigerator, it is more practical to take these parameters into account, rather than in reserve.
Tightness
Weak seals and mediocre thermal insulation of the housing contribute to the loss of cooled air. Poor sealing of the refrigerator means a constantly running compressor, and at the same time increased energy consumption.
Damaged rubber seal
Here it is better to give preference to proven brands. The model may be limited in functionality and other parameters, but well-known manufacturers never skimp on seals and insulation.
Influence of third party factors
In addition to direct factors, there are indirect factors that affect energy consumption indicators. To eliminate them, it is necessary to create optimal operating conditions for the device. The features of the latter are mentioned in the manual.
Energy consumption also depends on:
- temperature in the room where the refrigerator is installed;
- cell congestion level;
- timely service;
- door opening frequency.
Temperature
The acceptable operating environment for most refrigerators is +20⁰С. If the thermometer drops closer to 0, then energy consumption will increase up to 1.5 times. Extreme heat also has a negative impact on efficiency. At +30⁰C, the refrigerator will consume almost twice as much energy as it should.
Camera workload
Manufacturers strongly do not recommend loading equipment, which is called “to capacity.” Moreover, it is better to arrange the products evenly rather than stack them in one compartment, especially if they are at room temperature.
Timely service
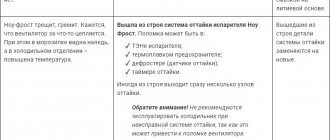
Here we are talking mainly about defrosting. If the device is not equipped with an automated melt ice removal system, then regular cleaning is extremely important. Snow crust in the chambers significantly reduces heat transfer qualities, thereby increasing energy consumption.
Snow coat in the refrigerator