The key to long-term and efficient operation of the air conditioner is its proper operation and regular maintenance. Do you agree? But in order to prevent breakdowns of this very expensive equipment, it is advisable to study the device and also consider the operating principle of the air conditioner.
It is these questions that we will discuss in our material - we will analyze in detail the main structural elements of standard climate control equipment. We’ll also talk about the principle and features of its functioning, and provide a typical diagram. We will supplement the article with visual photos and useful video recommendations.
Air conditioner device
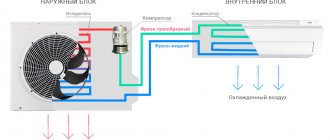
The operation of the device is based on the ability to absorb heat during evaporation and remove it through condensation. Let's take a closer look at how this procedure occurs in a split system.
Air conditioner circuit diagram
The main components of this unit are:
- Compressor.
- Evaporative element.
- Thermoregulation valve.
- Fans.
External unit
The air conditioner consists of an indoor and outdoor module, the latter is located outside the building. This is caused by the noisy operation of the fan and compressor, as well as the independent removal of warm air into the atmosphere.
Outdoor unit design
Despite the variety of air conditioners, their external module always has the same components:
- Compressor. It is capable of compressing freon and imparting a certain movement along the contour.
- Capacitor located in the outdoor unit. It turns the refrigerant into a liquid state.
- Evaporator. The radiator is located inside the device - it serves to convert freon from the watery phase to the gaseous state.
- Thermostatic valve (TRV). The device reduces the refrigerant pressure.
- Fans. The task of these devices is to blow air over the evaporator and condenser to create more intense heat exchange with the atmosphere.
- Filters. These parts of the air conditioner protect the circuit from foreign particles (dirt, dust)
IMPORTANT! When the air conditioner operates in warm air injection mode, the external module is equipped with a four-way valve, which is controlled from the internal module. It is responsible for changing the supply modes of warm and cold air flow.
Air conditioner operation in heating mode
Cassette air conditioner
Cassette air conditioners are similar in appearance to traditional fan coil units. But they have a significant difference. Freon circulates between the external and internal units, not water. The indoor unit has an evaporator through which air passes.
A cassette air conditioner can only be installed in a room where there are suspended or suspended ceilings. Moreover, the distance from the decorative to the real ceiling should be no less than the height of the indoor unit.
The big advantage of cassette air conditioners is uniform cooling of the room. Cold air is not directed in a specific direction, but spreads evenly over the area in all directions. The fence is carried out in the central part through a grate.
The operating principle of a cassette air conditioner.
Indoor unit
An indoor air conditioner is necessary to provide cool air in the room. The design of this unit allows you to take in air from the street and distribute it evenly in the room. In this regard, the main elements of the internal structure are:
Radiator (evaporator). It received this name because during the cooling stage freon evaporates in the tubes, and the principle of operation of the circuit is based on this phenomenon. The power of the unit largely depends on the size of this device: the larger the air conditioner, the larger the evaporator should be.
It is an interlacing of tubes with plates that increase the plane of heat transfer. The refrigerant moves through the capillary vessels at a certain speed and temperature.
Fan (impeller, shaft). To quickly cool the room, it is necessary to force the air flow through a cooled radiator. This is where this impeller helps.
For many models, the evaporator outlines the fan configuration, thereby making the installation of the internal module compact. This creates effective circulation of air masses.
Fan motor . It is attached with a special bracket to the module box and serves to rotate the impeller.
Drainage bath . During operation of the air conditioner, condensation forms on the radiator. And this tray exists to collect it. In addition to moisture, it collects dust, dirt and other foreign particles. Therefore, for better care, this device is removable.
Vertical and horizontal blinds. These elements move from small motors and are attached under the drainage tray. At the same time, horizontal curtains regulate the air flow up and down, and vertical ones - left and right.
Command block . This microcircuit is a board to which all significant starting elements of motors and sensors are connected through wires.
Coarse filter . It looks like a plastic mesh to which small particles of dust, dirt, and wool stick. This filter needs to be cleaned once every two weeks to avoid overloading the engine.
What is multi-split?
To provide a microclimate in different rooms, multi-zone air conditioners or multi-split systems were developed. The first models were introduced by Daikin in 1982. The technology was registered under the trade name Variable Refrigerant Volume, VRV, which translates from English as “variable refrigerant volume.”
Multi-split air conditioner consists of:
- Outdoor unit;
- Several indoor units;
- Regulatory systems.
The outdoor unit is responsible for cooling or heating freon using air from the street. Internal units regulate the speed and direction of airflow; they contain electronics responsible for the operating mode.
The general operating principle of a multi-zone air conditioner is based on the cycles of condensation and evaporation of the refrigerant. Read more about this in the sections The principle of operation of an air conditioner for cooling and The principle of operation of an air conditioner for heating . The differences lie in the distribution of freon into several flows.
The regulation system is a control unit connected to the outdoor and indoor units. It is responsible for freon distribution and signal processing. The system works as follows:
- The control unit receives a signal about the blowing speed and temperature from each indoor unit;
- The processor determines how much freon should be supplied to each individual unit;
- After calculations, the unit gives a signal to the external unit at what speed the compressor should operate (or how often it should turn on);
- When pumping refrigerant, the control unit distributes it between the indoor units.
There are basic configurations that include indoor units of the same type in a certain quantity, usually 3-5 pieces. (see illustration). Many companies offer non-standard solutions - you can select the required number of indoor units of different types. Such solutions are more expensive, but more practical.
Multi-split system with three indoor units.
Air conditioner operation
All components of the unit are connected to each other by copper tubes and thereby form a refrigeration circuit. Freon circulates inside it with a small amount of compression oil.
The air conditioner allows you to perform the following process:
- The compressor receives refrigerant from the radiator at low pressure of 2-4 atmospheres and a temperature of about +15 degrees.
- When working, the compressor compresses freon to 16 - 22 points, due to this it heats up to +75 - 85 degrees and enters the condenser.
- The evaporator is cooled by a flow of air having a temperature lower than that of freon, as a result of which the refrigerant cools and transforms from a gas into a watery state.
- From the condenser, freon enters the thermostatic valve (in household appliances it looks like a spiral tube).
- When passing through the capillaries, the gas pressure drops to 3-5 atmospheres, and it cools, while part of it evaporates.
- After the expansion valve, liquid freon enters the radiator, blown by an air flow. In it, the refrigerant is completely converted into gas, takes away heat, and therefore the temperature in the room decreases.
Then the freon with low pressure moves to the compressor, and all the work of the compressor, and therefore of the household air conditioner, is repeated again.
Air conditioner operation in cold weather
How does the air conditioning system work?
The operating principle of the air conditioner is based on the ability of substances to change their state of aggregation depending on pressure. All liquids, when evaporating (transitioning from a liquid to a gaseous state), absorb heat from the space surrounding them. During condensation (transition from a gaseous state to a liquid), heat, on the contrary, is released. The operation of the air conditioning system is impossible without gaseous hydrocarbons that contain fluorine, they are called freons . In general, substances that effectively remove heat when boiling and release heat when condensing are called refrigerants. Thanks to them, not only air conditioners work, but also any other refrigeration equipment.
On a note! Freons R-22 and R-410A are most often used in air conditioners. However, the first type is gradually falling out of use, as it has been established that it destroys the ozone layer. The second freon does not contain chlorine, it is not dangerous for the earth’s atmosphere, so manufacturers prefer it.
The boiling point of freon R-22 is -40.9 degrees Celsius, for R-410A it is -51.5. It is not easy to achieve such values in practice; additional cooling will be required. But this indicator is directly affected by pressure: the higher it is, the higher the temperature at which the liquid begins to boil. Therefore, to transition freons from one state to another, their pressure is changed to the required level using special devices.
Description of the operation of the air conditioner for cooling
The main components of the device are a compressor, a condenser, an evaporator and a thermostatic expansion valve (TEV) or electronic expansion valve. These components are connected in a closed circuit through which the refrigerant circulates.
Freon gas enters the compressor from the evaporator. The freon is under low pressure, just a few atmospheres, its inlet temperature is +10-20 degrees. The design of the compressor may be different, depending on the type of unit (screw, piston, rotary or spiral), but its purpose is always the same: to draw in gas, compress it and pump it into the next element of the circuit - the condenser. The freon pressure reaches one and a half to two dozen atmospheres or more (for a car air conditioner - about 12 atm), and the temperature rises to several tens of degrees above zero (+70-900).
On a note! A condenser is a radiator or heat exchanger made of finned tubes that are blown by a fan.
In the condenser, the heated gas passes through the tubes and cools, since its temperature is much higher than that of the air that washes the numerous elements of the heat exchanger. As a result, the freon condenses and releases heat. This is how liquid refrigerant comes out of the radiator, the pressure of which remains high, and the temperature decreases and becomes only a dozen or two degrees higher than that of the outside air.
The substance then passes through the expansion valve/expansion valve, which is also called a throttling device. It regulates the amount of refrigerant that is needed to maintain a certain level of evaporation to cool the room to a specific temperature. In this unit, the pressure and temperature of freon are reduced, as a result of which it turns into a mixture of liquid and gas.
Next, the refrigerant enters the evaporator, the heat exchanger of which may consist of tubes under the casing or plates with channels where freon moves. Here the liquid turns into a gaseous state and absorbs heat from the surrounding space. There is also a fan opposite this heat exchanger, so the air flow that passes through the evaporator is cooled. The gas is then sent back to the compressor.
Description of the operation of the air conditioner for heating
Air conditioners that operate according to the cycle described above cool the air. But there are also models that support heating - they have a four-way valve that redirects the movement of freon in the system . At the same time, the evaporator and condenser change places, so that warm air enters the room, and cold air, on the contrary, is discharged outside.
On a note! Air conditioning units that operate for heating are more expensive than cooling units.
Where does the air conditioner get its air from?
To answer the question of where the air conditioner gets its air from, you need to consider the following types of devices:
- supply air - they take air from the street;
- recirculation - use internal air;
- Recuperation air conditioners use a mixture of indoor and outdoor air.
Before purchasing climate control equipment, you should clarify exactly how the selected model takes in air. In the first and third cases, the room does not need to be regularly ventilated; in the second, on the contrary, you will need to periodically open windows or doors to maintain the amount of oxygen in the room at a comfortable level.
Types of air conditioners
Manufacturers produce all types of air conditioners, investing heavily in their business. As a result, a modern consumer can choose any model according to any parameters.
Air conditioners split systems
Split type devices are great for small rooms.
ON A NOTE! Based on installation, units are divided into floor, window, wall and ceiling air conditioners.
There are two types of such devices: separation systems and multi-dividing systems. Wall-mounted split system units consist of two blocks: a small internal unit and a large external module.
The external device contains the loudest devices. A multi split system is formed by combining several indoor units into a single outdoor module. This allows you to optimally preserve the design of the house.
Ceiling type air conditioners
In rooms with a large area, as a rule, units for installation on the ceiling are chosen. Their advantage is that the cooled air is evenly distributed horizontally throughout the room without directly affecting people.
A massive ceiling-type air conditioner is almost invisible, and it is indispensable when extensive air flow is needed to the most remote parts of the room, while the jet length in some models reaches up to 55 meters.
There are also duct and cassette ceiling air conditioners. In this case, the first devices are completely hidden behind a suspended ceiling or in a channel, and the second type - cassette blocks have the form of ceiling tiles measuring 600x600 mm.
Split system
Although the disconnect system consists of indoor and outdoor modules, its operating principle is no different from any other type of domestic ceiling air conditioner.
The housing of the external unit itself contains a heat exchanger, a fan and a compressor. Additional elements of the split system are a dryer, expansion valve and connecting pipes.
And also to connect the unit to the electrical network, it contains the necessary starting and control devices.
Industrial air conditioners
Such devices are developed to serve areas of more than 350 meters and therefore they have a number of features, thereby differing from household air conditioners. The design of precision equipment may vary.
They are often installed in houses where a special microclimate is needed for each room - shopping centers, banks, hotels. Industrial air conditioners are divided into the following systems:
Multizone devices. These VRF and VRV air conditioning units include up to 64 indoor modules and up to three outdoor units. In total, they are located on communications up to 300 meters long.
It is possible to set a separate temperature for each indoor module and provide its own microclimate in each room. The error in the set temperature is only 0.05 degrees.
"Chiller fan coil" . Devices with this system differ in that not freon is used inside the circuit, but water or antifreeze. The central refrigeration unit is called a “chiller”, and the heat exchange elements are called “fan coils”.
Chiller-fan coil circuit 2
The advantage of such a unit is that the distance between these components can be any, since water flows through ordinary pipes.
Central and rooftop air conditioners. These devices are varied in their action. They are used in the form of heat exchange units, fans, air purifiers and humidifiers.
It is called central because the air mass is processed in the indoor unit and then moves through pipes through the rooms. Installation of air conditioners of this type and installation of communications is particularly complex and requires an external source of cold.
If possible, it is better to choose roof monoblocks, which are easier to install.
Air conditioners and split systems
Devices that create a microclimate have a common name - air conditioners. Let's tell you what the difference is between air conditioners and split systems. Air conditioners can be made as a single unit or divided into indoor or outdoor units. In the first case, mobile or window air conditioners are usually used. The former can be moved indoors, but they have bulky pipes to move air. Window windows are installed in one block so that one side is located indoors and the other is located outside. They occupy part of the window opening and create noise during operation.
Split systems are divided into two blocks (compressor-condenser and evaporation), connected to each other by tubes and electrical wires. The noisiest part of the split system is located outside.
The use of such devices means fresh air and comfort Source vkrostov.ru
The difference also exists in terms of design. Window and mobile units are more bulky, and the internal parts of split systems come in a variety of shapes and colors and can often be installed on walls, floors or ceilings without disturbing the design of the room. Another difference is the possibility of not only cooling, but also heating the air.
A split system is more difficult to install. However, it offers more features and is more economical than conventional air conditioners.
Split systems are often installed in hotel rooms; what is it and what is it for? Let’s try to understand this in more detail.
Air conditioner malfunctions
Today's climate control equipment is equipped with a warning function about possible breakdowns. You just have to decipher the diagnostic information.
The unit does not turn on
This is the most common breakdown of an air conditioner and probably every user has encountered it. These problems usually occur due to the electrical part:
- The device is not connected.
- The command chip is faulty.
- There is no connection between the outdoor and indoor units.
- The control panel does not work.
- The circuit breaker has tripped.
- Incorrect switching when sending signals.
And finally, the device may fail due to simple wear and tear of parts.
Switching off the split system after a short period of operation
This phenomenon occurs due to overheating of the compressor, as well as due to a breakdown of the protective relay. The unit heats up due to contamination of the radiator on the external module.
In such cases, preventative cleaning of the grille should be carried out. And also after refueling, the balance in the radiator and condenser circuits may be disrupted.
Condensate leak from the indoor unit
In the summer, owners of air conditioners may experience overflowing of condensate containers. The reason for this may be freezing of the heat exchanger, which should be insulated. If leakage appears at the joints, then you need to tighten the nuts. If the drainage tube becomes clogged with dirt, it should also be cleaned.
The air conditioner is not working at full capacity
This type of malfunction occurs mainly in the summer. The device consumes a large amount of energy during operation, but is not able to provide the required temperature conditions. The reason here most often lies in dirty air filters.
ATTENTION! Although thin purifiers, ozonizers, and ultraviolet light lamps improve the air, they also significantly affect the cost of the unit.
Smells
If an unpleasant odor begins to appear from the device, there are several reasons for this. If there is a burning smell, you need to check the wiring, and it is recommended to do this at service centers.
When the stench gives off dampness or mold, it means that a colony of bacteria has formed inside the unit. You can get rid of it with the help of an antifungal drug.
Operating principle of a mobile (floor) air conditioner
Mobile air conditioners are made in the form of a monoblock. The compressor, condenser and evaporator are located in one housing. As with other types, heating or cooling of air occurs due to cycles of condensation and boiling of the refrigerant.
To cool or heat freon, an air flow is required, which must pass through the condenser. There are two types of mobile air conditioners:
- With one air duct;
- With two air ducts.
A mobile air conditioner with a single duct draws air from the room, blows it through the condenser and blows it out. The air duct is discharged through any opening in the wall, partition, etc. The best option is to use special plugs in windows with a vertical frame.
This single duct system has a big drawback. It pumps out air and creates draft. Therefore, air comes from other rooms through doors, ventilation systems, and openings. The air coming from outside is usually warmer. Due to this, energy consumption increases.
Mobile air conditioner with one air duct.
A system with two air ducts does not have this disadvantage. It has two hoses that lead outside. A mobile air conditioner takes air through one duct, passes it through a condenser and blows it out through another duct.
The operating principle of a mobile air conditioner with two air ducts allows you not to pump air out of the room. Therefore, cooling occurs more efficiently. Its energy consumption is lower.
Mobile air conditioner with two air ducts.
Modern mobile air conditioners can work for heating. But problems arise during installation. The installation sites of air ducts must be insulated. It is advisable to protect the hoses themselves with thermal insulation.
The benefits and harms of air conditioning
>Pros of the device
The main advantage of air conditioners is that they create a microclimate suitable for humans in the room. This, in turn, increases labor productivity, improves mood and well-being.
Therefore, the main advantage of this air conditioner is the creation of favorable conditions for work or leisure. The main task of such units is to lower the temperature during hot periods and heat the air during cold periods.
In addition, installing air conditioners in service centers or in Internet rooms allows you to avoid premature breakdowns of computer equipment due to overheating.
And also some models of such units are capable of performing several more useful functions:
- Purifying the air space from unpleasant odors. For example, window air conditioners are often installed in the kitchen and toilet.
- Humidification or dehumidification of indoor air.
Disadvantages of devices
However, if the air conditioner is used incorrectly, it can cause certain harm to human health:
- There is a possibility that these devices may harbor harmful bacteria.
- Climate control equipment favors the spread of viruses.
- Air conditioners, passing air through themselves, kill useful elements in it.
- Compressors create noise during operation.
In fact, in most cases, this refers to myths, and such statements are not true. To avoid unpleasant phenomena, you do not need to be under a cold stream of air flow.
Systematic cleaning of the unit and its preventive repairs will help avoid improper operation of the device. And if you follow these basic rules, the air conditioner will create a pleasant microclimate in the room, which is so necessary for a person to have a pleasant rest and fruitful work.
Mobile air conditioner without hoses
There are mobile floor air conditioners without hoses. Their system does not use refrigerant; they work by forced evaporation of water. The operating principle of such a mobile air conditioner is as follows:
- Air is drawn from the room by a fan;
- It passes through a filter that traps dust and dirt;
- A stream of air is blown through a membrane moistened with water;
- Moisture particles evaporate from the membrane, its temperature drops and cools the air;
- Humidified and cooled air enters the room.
The principle of operation of a mobile air conditioner without hoses and air ducts.
There are large, fully functional models. Their cost is lower than that of conventional mobile air conditioners that use freon to produce cold. But the efficiency is much lower.
Depending on the power of the evaporative air conditioner and the volume of the room, it can reduce the temperature by 1-5 degrees in 1 hour. It does a good job of maintaining the temperature in a chilled room.
The disadvantage of such air conditioners is constant air humidification. Due to low efficiency, they must be constantly running. Due to this, humidity increases. This can negatively affect your well-being; drops of water condense on furniture and household items.
In recent years, mini air conditioners such as Arctic Air have appeared. Manufacturers and sellers talk about their effectiveness, but in practice it is a hoax. With small sizes and low power, they can cool a room of no more than 2 sq.m. area. Read more about their “efficiency” in the article: Arctic Air mini air conditioner: reviews, deception of sellers and principle of operation.
There are high power models that are used for centralized cooling. They also serve as a ventilation system. This evaporative air conditioner takes air from outside the home, cools it, and delivers it inside.